Subjunctive in noun clauses spanish – The subjunctive in noun clauses is a fundamental grammatical concept in Spanish that adds nuance and precision to speech and writing. This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, usage, and intricacies of the subjunctive in noun clauses, providing a thorough understanding for learners of all levels.
The subjunctive mood is employed in noun clauses to express uncertainty, doubt, possibility, or emotion. Understanding its grammatical rules and common verb usage is essential for accurate and effective communication in Spanish.
Definition and Usage

The subjunctive mood in Spanish is a grammatical mood that expresses a hypothetical or uncertain action or state of being. It is used in noun clauses, which are clauses that function as nouns within a sentence.
There are two main grammatical rules for using the subjunctive in noun clauses:
- The subjunctive is used after verbs that express doubt, uncertainty, or emotion.
- The subjunctive is used after conjunctions that introduce noun clauses, such as “que” (that), “para que” (in order that), and “aunque” (although).
Types of Noun Clauses
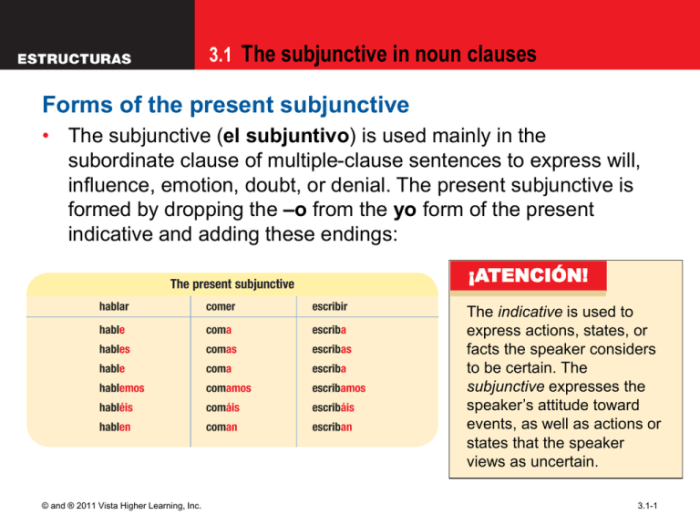
Noun clauses that can use the subjunctive mood fall into three main categories:
- Substantive noun clauses: These clauses function as nouns within a sentence, acting as the subject, direct object, indirect object, or complement.
- Adjective noun clauses: These clauses modify or describe a noun or pronoun.
- Adverbial noun clauses: These clauses function as adverbs, modifying verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Substantive Noun Clauses
Substantive noun clauses can perform various functions within a sentence:
- Subject: Es importante que estudies mucho.(It is important that you study a lot.)
- Direct object: Quiero que vengas conmigo.(I want you to come with me.)
- Indirect object: Le pedí que me ayudara.(I asked him to help me.)
- Complement: Mi sueño es que sea feliz.(My dream is for him to be happy.)
Adjective Noun Clauses
Adjective noun clauses modify nouns or pronouns, providing additional information or description:
- El libro que estoy leyendo es muy interesante.(The book that I am reading is very interesting.)
- La mujer que vi ayer es mi vecina.(The woman that I saw yesterday is my neighbor.)
Adverbial Noun Clauses, Subjunctive in noun clauses spanish
Adverbial noun clauses modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, expressing various adverbial functions:
- Purpose: Vine aquí para que me ayudes.(I came here so that you could help me.)
- Reason: Estoy triste porque no puedo ir.(I am sad because I cannot go.)
- Result: Habló tan alto que todos lo oyeron.(He spoke so loudly that everyone heard him.)
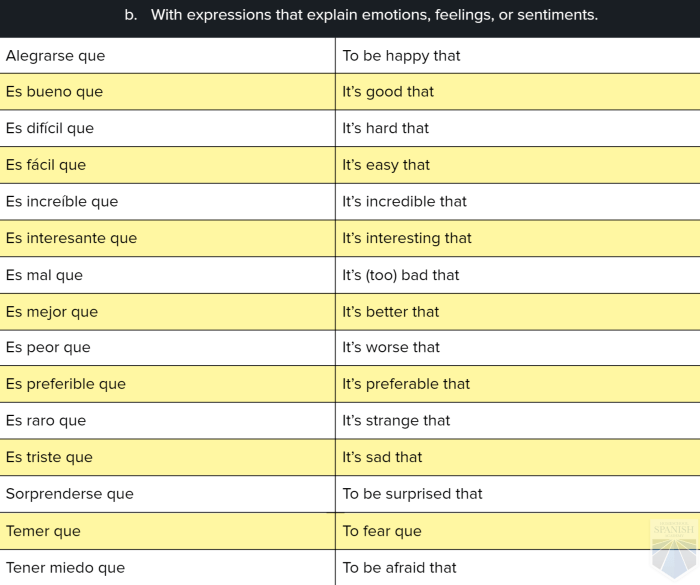
Common Verbs in Noun Clauses

The subjunctive mood is used in noun clauses to express a variety of meanings, including uncertainty, possibility, desire, and emotion. Certain verbs are commonly used in noun clauses that require the subjunctive mood.
The following table lists some of the most common verbs used in noun clauses that require the subjunctive mood, along with their infinitive, present indicative, and present subjunctive forms:
| Infinitive | Present Indicative | Present Subjunctive |
|---|---|---|
| alegrar | alegra | alegre |
| creer | cree | crea |
| dudar | duda | dude |
| esperar | espera | espere |
| imaginar | imagina | imagine |
| lamentar | lamenta | lamente |
| negar | niega | niegue |
| pedir | pide | pida |
| pensar | piensa | piense |
| preferir | prefiere | prefiera |
| querer | quiere | quiera |
| recomendar | recomienda | recomiende |
| rogar | ruega | ruegue |
| sentir | siente | sienta |
| sugerir | sugiere | sugiera |
| temer | teme | tema |
Practice Exercises
Practice exercises are essential for students to test their understanding of the subjunctive in noun clauses. These exercises can help students identify the correct verb form, complete sentences, and translate sentences from English to Spanish.
There are many different types of practice exercises that can be used to teach the subjunctive in noun clauses. Some common types of exercises include:
- Identification exercises:These exercises require students to identify the correct verb form in a noun clause.
- Completion exercises:These exercises require students to complete sentences with the correct verb form in a noun clause.
- Translation exercises:These exercises require students to translate sentences from English to Spanish, using the correct verb form in noun clauses.
Practice exercises can be used in a variety of ways. They can be used as homework assignments, in-class activities, or review materials. They can also be used to assess students’ understanding of the subjunctive in noun clauses.
Helpful Answers: Subjunctive In Noun Clauses Spanish
What is the subjunctive mood?
The subjunctive mood is a grammatical mood used to express uncertainty, doubt, possibility, or emotion.
When is the subjunctive used in noun clauses?
The subjunctive is used in noun clauses that express uncertainty, doubt, possibility, or emotion.
What are some common verbs used in noun clauses that require the subjunctive?
Some common verbs used in noun clauses that require the subjunctive include creer (to believe), pensar (to think), dudar (to doubt), and esperar (to hope).