Welding principles and applications eighth edition – Delve into the Eighth Edition of Welding Principles and Applications, a comprehensive guide that illuminates the fundamentals of welding, empowering you to harness the transformative power of this essential craft. This definitive resource provides an in-depth exploration of welding processes, equipment, techniques, safety protocols, and diverse industrial applications, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to excel in the dynamic field of welding.
Welding Principles
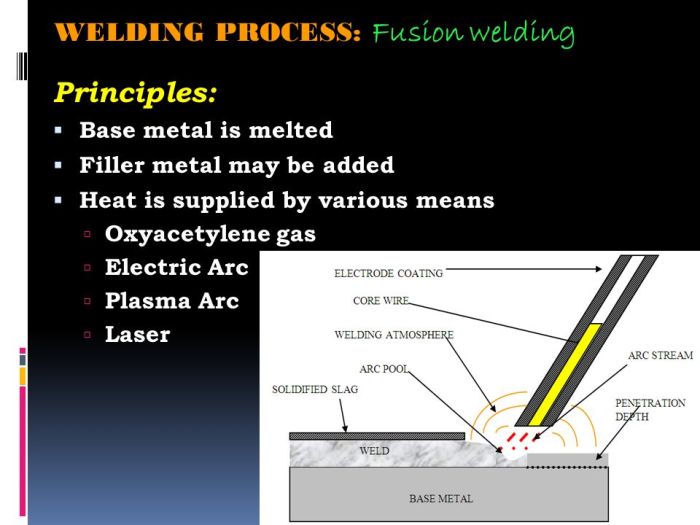
Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing fusion. The most common welding process is arc welding, which uses an electric arc to melt the materials together. Other welding processes include gas welding, resistance welding, and laser welding.
Welding is used in a wide variety of applications, including construction, manufacturing, and repair. It is an essential skill for many tradespeople, including welders, fabricators, and engineers.
Types of Welding Processes
- Arc welding
- Gas welding
- Resistance welding
- Laser welding
Examples of Welding Applications, Welding principles and applications eighth edition
- Construction of bridges and buildings
- Manufacturing of cars and airplanes
- Repair of pipelines and machinery
Welding Equipment and Materials: Welding Principles And Applications Eighth Edition
The type of welding equipment and materials used will depend on the welding process being used. For example, arc welding requires a welding machine, welding electrodes, and shielding gas. Gas welding requires a welding torch, welding gas, and welding rods.
Types of Welding Equipment
- Welding machines
- Welding torches
- Shielding gas
- Welding rods
Properties and Uses of Different Welding Materials
The properties of welding materials, such as their strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, will determine their suitability for different applications. For example, mild steel is a common welding material used in construction because of its strength and low cost. Stainless steel is a more expensive welding material, but it is more corrosion-resistant than mild steel.
Tips for Selecting the Right Welding Equipment and Materials
- Consider the type of welding process being used.
- Consider the materials being welded.
- Consider the desired strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance of the weld.
- Consult with a welding expert if necessary.
Welding Techniques

There are a variety of welding techniques that can be used to create different types of welds. The most common welding technique is the shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process, which uses a consumable electrode to create an electric arc between the electrode and the workpiece.
Other welding techniques include gas metal arc welding (GMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW).
Basic Welding Techniques
- Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)
- Gas metal arc welding (GMAW)
- Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW)
- Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW)
Advanced Welding Techniques
- Submerged arc welding (SAW)
- Electroslag welding (ESW)
- Laser beam welding (LBW)
- Electron beam welding (EBW)
Table Comparing Different Welding Techniques
| Welding Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| SMAW | Versatile and inexpensive | Slow and requires a skilled welder |
| GMAW | Fast and easy to learn | Can produce spatter and fumes |
| GTAW | Produces high-quality welds | Slow and requires a skilled welder |
| FCAW | Versatile and fast | Can produce spatter and fumes |
Welding Safety

Welding is a hazardous occupation, and it is important to take precautions to prevent accidents. Welding safety hazards include electric shock, burns, fumes, and eye injuries.
Importance of Welding Safety
- To prevent accidents
- To protect the welder and others from injury
- To comply with safety regulations
Different Welding Safety Hazards
- Electric shock
- Burns
- Fumes
- Eye injuries
Tips for Preventing Welding Accidents
- Wear proper protective clothing and equipment.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Follow all safety procedures.
- Be aware of the hazards associated with welding.
Welding Applications
Welding is used in a wide variety of applications, including construction, manufacturing, and repair. It is an essential skill for many tradespeople, including welders, fabricators, and engineers.
Different Industries That Use Welding
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Repair
Specific Welding Applications in Each Industry
Construction
- Building bridges
- Erecting skyscrapers
- Repairing pipelines
Manufacturing
- Building cars
- Manufacturing airplanes
- Producing appliances
Repair
- Fixing cars
- Repairing machinery
- Welding broken pipes
Common Welding Projects
- Welding a metal fence
- Building a welding table
- Repairing a car exhaust system
Welding Education and Training
There are a variety of welding education and training programs available. These programs can help you learn the skills you need to become a welder.
Different Welding Education and Training Programs
- Vocational schools
- Community colleges
- Private welding schools
- Online welding courses
Benefits of Welding Certification
- Increased job opportunities
- Higher wages
- Improved safety
Tips for Finding a Welding Job
- Network with other welders.
- Attend job fairs.
- Apply for jobs online.
- Contact welding companies directly.
FAQ Explained
What are the fundamental principles of welding?
Welding involves joining materials by melting their surfaces and fusing them together. Heat is generated through various processes such as electric arcs, flames, or lasers.
What are the different types of welding processes?
Common welding processes include arc welding (e.g., MIG, TIG, stick), gas welding (e.g., oxy-acetylene), and solid-state welding (e.g., friction welding, ultrasonic welding).
What are the essential safety precautions for welding?
Welders must wear appropriate protective gear (e.g., helmets, gloves, aprons) to shield themselves from intense heat, sparks, and harmful fumes. Proper ventilation and adherence to safety protocols are crucial to minimize risks.