As a group of biologists is studying the competitive relationships between organisms takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authority, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. The concept of competition in the context of biology, along with its various types and influencing factors, will be explored in-depth, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental ecological phenomenon.
The subsequent paragraphs will delve into the methodologies employed by researchers to study competitive relationships, examining both experimental and observational approaches. The challenges and limitations of studying these relationships in natural environments will also be discussed, highlighting the complexities involved in unraveling ecological interactions.
Competitive Relationships Among Organisms

Competition is a fundamental ecological interaction that occurs when organisms seek to obtain limited resources. It can take various forms, including:
Types of Competition
- Interspecific competition:Competition between individuals of different species for the same resources.
- Intraspecific competition:Competition between individuals of the same species for the same resources.
The intensity of competition is influenced by factors such as resource availability, population density, and the degree of niche overlap between species.
Methods for Studying Competitive Relationships

Researchers use various methods to study competition, including:
Experimental Methods
- Field experiments:Manipulating resources in natural environments to observe the effects on competition.
- Laboratory experiments:Controlling variables in artificial settings to isolate the effects of competition.
Observational Methods
- Field observations:Monitoring interactions between species in natural environments.
- Comparative studies:Comparing the characteristics and distribution of competing species.
Challenges in studying competitive relationships include identifying the specific mechanisms of competition and separating their effects from other environmental factors.
Examples of Competitive Relationships in Different Ecosystems
Competition occurs in diverse ecosystems, including:
Terrestrial Ecosystems
- Competition for water and nutrients between plants in deserts.
- Competition for food between predators and their prey.
Aquatic Ecosystems
- Competition for light and nutrients between phytoplankton.
- Competition for food between fish species.
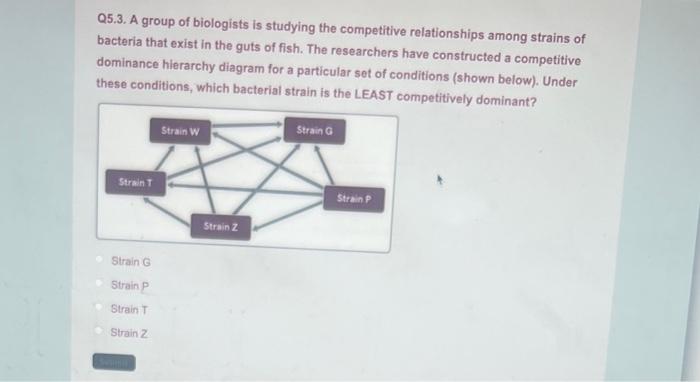
Marine Ecosystems, A group of biologists is studying the competitive relationships
- Competition for space and food between corals and sponges.
- Competition for prey between marine mammals and seabirds.
Competition shapes the distribution and abundance of species within ecosystems.
The Impact of Competition on Evolution: A Group Of Biologists Is Studying The Competitive Relationships
Competition drives natural selection by favoring individuals with traits that enhance their competitive ability. These traits include:
- Morphological adaptations:Physical characteristics that enhance resource acquisition or defense.
- Behavioral adaptations:Strategies for avoiding or reducing competition.
- Physiological adaptations:Enhanced resource utilization or tolerance to competitive stress.
Competition has played a crucial role in the diversification of life on Earth.
Management Implications of Competitive Relationships
Understanding competitive relationships can inform conservation and management practices, such as:
Conservation
- Identifying and protecting key resources to reduce competition and support biodiversity.
- Managing invasive species that outcompete native species.
Management
- Manipulating competition to control pests or promote beneficial species.
- Designing agricultural systems that minimize competition between crops and weeds.
Understanding competition is essential for managing ecosystems and achieving conservation goals.
Clarifying Questions
What is the concept of competition in biology?
Competition occurs when organisms utilize the same limited resources, such as food, water, or shelter, leading to a struggle for survival and reproduction.
What are the different types of competition?
Competition can be classified into two main types: interspecific competition, which occurs between individuals of different species, and intraspecific competition, which occurs between individuals of the same species.
What factors can influence the intensity of competition?
The intensity of competition can be influenced by factors such as resource availability, population density, and the degree of niche overlap between competing species.